The appearance of a new life is always a charming, but at the same time frightening moment, as future parents rejoice in pregnancy, and at the same time try to protect the fetus from any troubles in order to get a healthy child. Today we will talk about the heart rate (HR) of the fetus, changes in heartbeat by week of life according to the table, and also learn how to determine the rhythm of the heart using various devices.
First heartbeat
The child’s organs and organ systems form slowly and gradually, and at the initial stage they do not always function. It is impossible to determine the exact moment of the first heartbeat in the fetus because individual parts of the heart begin to contract even before the organ is fully formed.
Such contractions do not occur due to impulses emanating from the nervous system, and do not in any way affect the general condition of the baby. It turns out that the small heart begins to contract even before it acquires a “finished” appearance, so you will not be able to see or hear the first echoes of the heart’s work, and you will not be able to determine exactly when they appear.  The “true” heartbeat can be heard at 6-8 weeks, however, in very rare cases this may happen up to a week earlier.
The “true” heartbeat can be heard at 6-8 weeks, however, in very rare cases this may happen up to a week earlier.
Did you know?After 4 weeks, the fetus develops a real tail, which disappears after 8 weeks of pregnancy, so our tailbone is nothing more than an underdeveloped tail.
Determination methods
To determine when the embryo’s heart begins to beat, various diagnostic methods are used that allow the expectant mother and doctors not only to see the fetal body, but also to compare the data on the contraction of its heart with the norms.
First, let's figure out what an ultrasonic device is and how it works.
The device operates exclusively on sound waves that penetrate tissue, air-filled cavities, and bones. In this case, the propagation of waves depends on the density of the medium. Waves that touch various objects are reflected in the opposite direction, after which they are picked up by the receiver. It turns out that on the ultrasound screen we see nothing more than a sequential reflection of the waves that form the pattern.  To make it easier to understand, let’s draw a parallel with fluorography. When a photo is taken, the device releases particles at high speed that penetrate the body. They can pass through tissue, but do not pass through bones and some organs, as well as tissue compaction. Those particles that have passed through your body leave a white trace, and the empty spaces remain dark. So, waves, unlike particles, do not stop on bones and obstacles, but are reflected in the opposite direction, which allows you to see the picture.
To make it easier to understand, let’s draw a parallel with fluorography. When a photo is taken, the device releases particles at high speed that penetrate the body. They can pass through tissue, but do not pass through bones and some organs, as well as tissue compaction. Those particles that have passed through your body leave a white trace, and the empty spaces remain dark. So, waves, unlike particles, do not stop on bones and obstacles, but are reflected in the opposite direction, which allows you to see the picture.
Important! Ultrasound is completely harmless, unlike fluorography.
Ultrasound examination helps to detect the heartbeat, since the sound travels well through the bladder. Wherein There are 2 ways to perform ultrasound of the fetal heart during pregnancy: transvaginal and transabdominal.  The first option involves inserting a sensor into the vagina, which makes it possible to detect a heartbeat already at 5-6 weeks. The second option involves placing the sensor on the mother's abdomen. In this case, the heartbeat can be determined only at 6-8 weeks. This diagnostic method helps not only to compare the number of organ beats with the norms, but also to identify heart defects.
The first option involves inserting a sensor into the vagina, which makes it possible to detect a heartbeat already at 5-6 weeks. The second option involves placing the sensor on the mother's abdomen. In this case, the heartbeat can be determined only at 6-8 weeks. This diagnostic method helps not only to compare the number of organ beats with the norms, but also to identify heart defects.
It is a more advanced version of ultrasound, which also uses sound waves to determine the condition of the organ.
Echocardiography is different in that it allows not only to determine the heart rate (HR), but also to provide comprehensive information related to the thickness of the heart muscle, the condition of the tissues and valve apparatus, and also allows you to see the work of the heart in real time, not in a two-dimensional version, but in 3D.
This method not only shows a good picture, but also allows you to obtain many times more important information than the standard version of ultrasound, so it is used to identify hidden heart defects, as it allows specialists to even trace the speed of blood movement in the ventricles of the organ. 
Important! Echocardiography is performed only if the mother has any health problems, is over 38 years old, or the children born have had heart problems.
Since the above methods cannot be used for diagnosis during every appointment, doctors use the simplest diagnostic option - listening. That is: the doctor takes a stethoscope, after which he puts one end to the woman’s stomach, and puts his ear to the other.
This method of listening can only be used from 18-20 weeks of pregnancy, since up to this point the sound of the heartbeat is so weak that it cannot be heard using this method.  Although auscultation seems like a thing of the past, it helps to hear not only the rhythm of the heart contraction, but also other sounds that indicate the presence or absence of problems associated with neighboring organs (intestines, aorta, uterine vessels).
Although auscultation seems like a thing of the past, it helps to hear not only the rhythm of the heart contraction, but also other sounds that indicate the presence or absence of problems associated with neighboring organs (intestines, aorta, uterine vessels).
Cardiotocography is an analogue of an ECG, however, in this case, the frequency of contraction of the heart of the fetus and the mother’s uterus is examined. The device displays graphic material on the tape, from which you can find out how fast the heart beats, how strongly the uterus contracts, and how often the rhythm changes.
There are two types of CTG: direct and indirect.
With the indirect method, sensors are attached externally in those places where the rhythm is best heard (the first is at the fundus of the uterus, the second is in places where heartbeats are stable recorded).
The direct method is used only when the integrity of the fruit bladder is broken. In this case, one spiral electrode is inserted into the presenting part of the fetus, and the second sensor in the form of a catheter is inserted into the uterus.  This method is used to obtain accurate data that is immediately displayed on a paper tape, as is the case with an cardiogram.
This method is used to obtain accurate data that is immediately displayed on a paper tape, as is the case with an cardiogram.
Heart rate norms by week
- this is the period from conception to the 13th week inclusive, therefore, we will consider several periods during which the rate of contraction of the heart muscle changes.
class="table-bordered">
In the first trimester, the foundations of organ systems are laid, and the most important organs are formed, which is why the number of beats per minute changes. In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, heart rate normalizes and remains at the same level.
Many people are interested in the question of how many beats per minute a healthy baby’s heart should beat. At the initial stage, it all comes down to the newness of the equipment, the exact date of pregnancy, as well as the general condition of the mother. As you can see, the difference between 4 and 9 weeks is more than significant, so you should understand that the doctor is guided by the standards in accordance with the stage of pregnancy.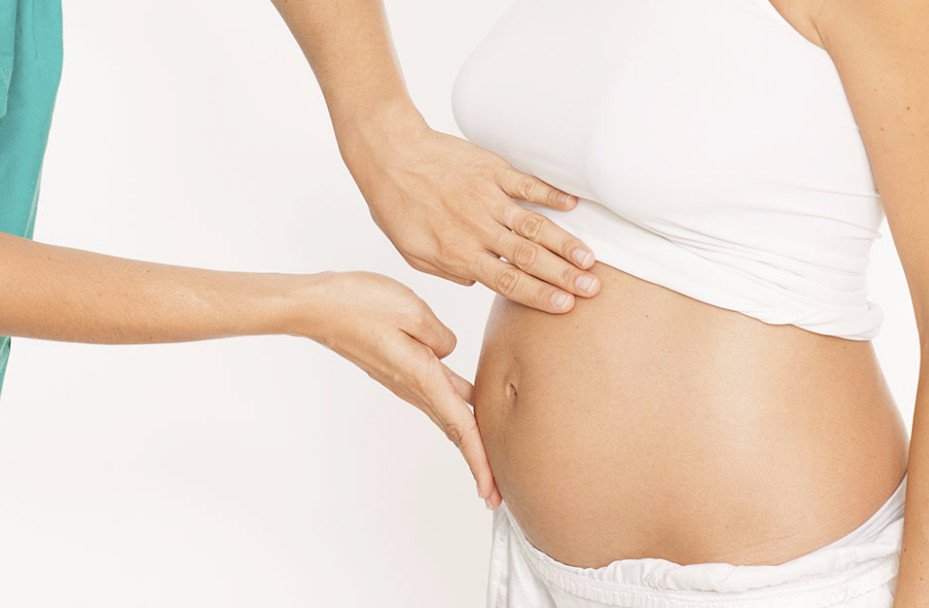  That being said, there are a few points worth discussing. If the heartbeat does not increase with the period, there is a risk of losing the baby in the early stages. That is, if at 5-6 months the heart rate is 80 beats or less, it means something is wrong with the fetus.
That being said, there are a few points worth discussing. If the heartbeat does not increase with the period, there is a risk of losing the baby in the early stages. That is, if at 5-6 months the heart rate is 80 beats or less, it means something is wrong with the fetus.
If in the early stages the heartbeat accelerates to 170 or higher, it means that the problem is associated with a violation of the location of the placenta, which threatens internal bleeding, as well as miscarriage.
Sometimes it happens that the heartbeat is normal, but it is very hard to hear. This occurs due to the old age of ultrasound machines, obesity in the mother, or due to heart defects in the fetus.
If there is no shock at all, then old equipment is to blame. However, this may also indicate a frozen pregnancy (stagnation of development and death).
- this is 14-27 weeks of pregnancy. In the second trimester, the baby’s development does not proceed so rapidly; its organs do not undergo major changes.  From the 13th week until birth, the fetal heart beats at a speed of 140-160 beats per minute, so next we’ll talk specifically about deviations from the norm.
From the 13th week until birth, the fetal heart beats at a speed of 140-160 beats per minute, so next we’ll talk specifically about deviations from the norm.
In the second trimester, the heartbeat normalizes, so if the doctor diagnoses a heart rate below 120 beats, this may mean chronic fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen) or compression of the umbilical cord.
If the heart rate exceeds 170 beats per minute, a specialist can diagnose the following: hypoxia, or a reaction to the mother’s emotional turmoil.
A dull heartbeat in the second trimester indicates the following problems: fetoplacental insufficiency (the mechanism for providing the fetus with necessary substances is disrupted), the location of the placenta on the anterior wall, polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios, heart problems.
The absence of a heartbeat indicates the death of the fetus or a malfunction of the device.
Did you know? They were able to determine pregnancy by the presence of the hormone in the urine at the beginning of the 20th century. At that time there were no special tests, so the methods were “barbaric”. Pregnant urine was injected into female mice or rabbits; After some time, the animals were killed, after which the ovaries were examined.
Third trimester
 At , as mentioned above, heart rate remains at the same level - accordingly, the above deviations remain unchanged. An increase or decrease in heart rate indicates the same problems as in the second trimester.
At , as mentioned above, heart rate remains at the same level - accordingly, the above deviations remain unchanged. An increase or decrease in heart rate indicates the same problems as in the second trimester.
Separately, it is worth mentioning that the norms do not take into account the characteristics of the mother’s body and the conditions of fetal development, so many children with a low or high heart rate are born healthy.
Now you know what the fetal heartbeat should be like by week, you are familiar with the heart rate table, and you know how the devices that allow you to hear the first heartbeats work. Remember that any norm is not an axiom, so there is no need to panic if minor deviations are detected in a child. Health to you and your baby!